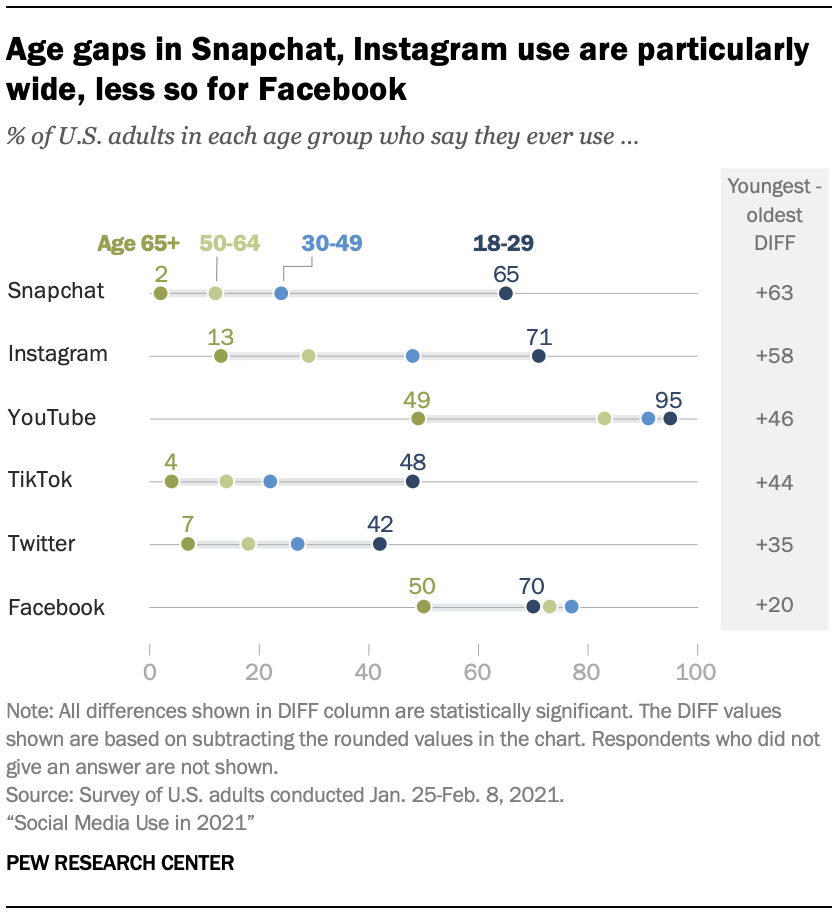
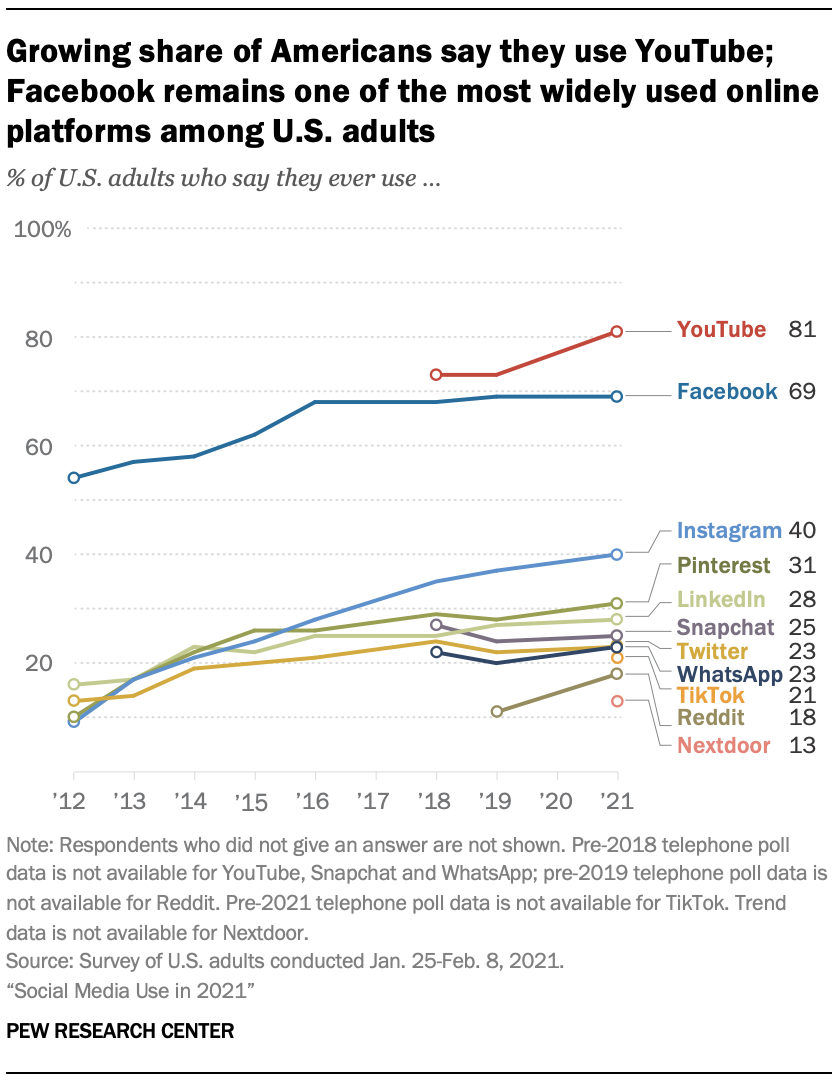
The Complete Guide to Contextual Targeting: How it Works and Why It is The Solution for a Cookie-less Marketing
Contextual Targeting Guide – Contextual vs. Behavioral Examples. Every marketer wants to produce ads that will reach the right customer at the right time. Contextual targeting has been making waves as the next solution for achieving that.
This post cover essential details of contextual targeting, from what it is to why it is important. Additionally, we feature best practices and the top platforms you can use.
In this post
What Is Contextual Targeting?
The definition of contextual targeting is an advertising method that involves display ads relevant to the user by considering the context of the website and the user’s interests. It differs from behavioral advertising techniques, which target specific users based on browser history.
What Is Contextual Targeting in Advertising?
| Contextual targeting is a targeted and automated form of digital advertising. It allows advertisers to display ads that are relevant to the website’s content instead of using visitors’ data. |
The idea has been around quite some time, for example, the half-page baby carrier ads next to an article about newborns in a parenting magazine. Contextual ads for digital advertising work similarly by targeting the content on the site instead of the user’s data.
In the decades before digital advertising, editors and designers spent a lot of time assembling and curating the ads to go with the content. Today, this process is entirely automated. Since the early days of the internet, advertising technologies have enabled advertisers to segment and target their audiences according to their behavior and interests.
These days, with privacy regulations becoming more strict, contextual targeting is gaining popularity because it relies on context, and not on personal data.
Types of targeting
Understanding contextual targeting is helpful if we compare it with other methods. There are many types of ad targeting for ad campaigns. Let’s review the five most popular practices of targeting.
- Behavioral targeting
An example of behavioral targeting is retargeting ads. This practice segments customers based on their browsing behavior. The segmentation may include the pages the user visited, the searches they performed, what links they clicked on, and which products they purchased. Some platforms also consider location and in-store purchases—the system groups visitors with similar behaviors into audience segments. An example of behavioral targeting is retargeting ads.
- Contextual targeting
This method involves displaying ads based on a website’s content. For example, you are placing an ad for running shoes on a forum for runners. Contextual targeting works by assuming someone visiting a site about running will probably be interested in buying other types of utility shoes.
- Search retargeting
Search retargeting comprises serving to display ads to users when browsing the web, according to their keyword search behavior. When you set up a search ads campaign, you choose the keywords that apply to your business or products. For example, a company selling women’s shoes serves ads to searchers looking for “women’s boots” or “black heel evening shoes.”
- Site retargeting
The most common form of retargeting consists of showing ads to users who visited your website but left without completing a purchase or taking action. Because it targets brand recognition, this method can bring a high ROI by targeting the bottom part of the funnel.
- Predictive targeting
Predictive targeting uses data collected by behavioral targeting, adds a bit of 3rd party data into the mix, and analyzes and predicts buying patterns with the help of artificial intelligence and machine learning. The artificial intelligence feature can detect behavior patterns, identify products to upsell and cross-sell, and target which shoppers are most likely to convert.
Behavioral Targeting vs. Contextual Targeting
The differences between contextual and behavioral targeting reside in what method considers to select the ads that will be displayed:
- Contextual targeting selects the ads to serve according to the website’s context and content. Its goal is to increase the ads’ relevance to the user.
- Behavioral targeting selects the ads according to the user’s historical browsing data Behavioral targeting relies heavily on data analytics and data processing. Its goal is to achieve personalized behavioral targeting.
Let’s review the main differences between contextual and behavioral targeting.
So, which one should you use? Marketers usually use a mix of both to target their audience effectively.
Marketers usually combine different audience targeting methods to gain the user’s attention. Contextual and behavioral targeting are two of the most popular methods. These terms are also referred to as contextual and behavioral advertising.
Both contextual and behavioral targeting have the same goal: ensuring that the right ad is placed in front of the user who is most likely to purchase. The issue with behavioral targeting is that technique is based on past consumer behavior to predict future actions. On the other side, contextual targeting targets campaigns by placing ads on the website the buyer may end.
How Does Contextual Targeting Work?
Automation gives contextual targeting the efficiency it needs to address digital advertising. Let’s check how it works:
Contextual targeting solutions use a web crawler to scan the website URLs and categorize the content. The goal of this is to understand the site and how it may respond to visitor queries. When a user visits a website page, the information collected by the crawler is passed in the request to the ad server. The ad server matches relevant campaigns to the topic categories, keywords, and more.
Unlike behavioral targeting, in contextual targeting, the publisher’s ad server fetches page-level data, querying the URL and placement IDs, and passes it to AdTech platforms. These platforms then select suitable ads that match the context of the page. Since users get to the page driven by their answers, contextual ads enhance their experience.
So, what are the steps for setting up contextual targeting?
Before starting, you should tell the system which factors to consider when choosing where to place your ads.
1. Choose a topic and a keyword.
The first step is to choose the topic of your campaign and what keywords it will use.
-
What’s a topic?
A topic is a broad category for your campaign, such as fashion, business, technology, house, garden, etc. When you elect one of them, your ad can run on Google’s Display Network’s sites related to this topic.
For example, you can start broad, like “Fashion,” then refine it into “Shoes.”
-
What is a keyword?
Keywords are words that help the network match your ads to website content. A keyword can be a single word or a short phrase. Google recomemnds each campaign should use between 5 to 50 keywords.
For example, int he case of our shoes campaigns you can include words about the shoe styles you want to promote, like “open toed sandal”, “hiking boots”, and also phrases customers would use when looking for shoes online, such a “shoes for weddings”.
2. Choose your contextual audiences
You can refine your ads setup by selecting the audience you want your ads to be served. Filter by location, and other demographic factors to ensure your ads get to the right users.
3. Place your Ads on Google.
Once you finish setting up your preferences and keywords, you can place your ads in Google. The ad network will search among the registered web pages to see if the content on any of them matches your keyword and topics, then display the ads on relevant webpages.
WHAT SHOULD YOU BE CAREFUL OF? A WORD TO ADVERTISERS
As an advertiser, you should be careful when you place your order on your ad network. For instance, when you order with Google Ads, the platform analyzes the content on every page on their network to find the most relevant content for your ad. It will analyze the written content, page structure, link structure, and keywords, among other factors.
The network uses the keywords and topics of your ad groups to select where to show your ads. The network will look at the keywords first before considering other factors. Therefore, the ads will appear only on pages related to your keywords.
Another factor you need to consider is the reach you want to achieve with your ad. If you set your display network setting to broad reach, the network will first place the ad according to your topic. If you choose a specific reach, the system will rely on your keywords and targeted topics to select a match for your ad.
What is keyword contextual targeting?
Ad networks like the Google Display Network use keyword targeting to match keyword-targeted ads to sites. Keyword targeting is a form of contextual targeting that is better for advertisers looking for performance.
How does keyword targeting work? The platform serves the ads according to keywords previously set by you on your campaign setup. When users search for topics related to those keywords, they get relevant ads.
You can learn more about how this works for Google Display Network here.
Contextual Ads Examples
Let’s go through the process of placing a contextual ad by giving an example:
First, you should choose keywords and topics.
| Example of setting up an ad group by keyword:
Let’s say you create an ad group to advertise your animal shelter, and you include keywords like dogs, pets, and cats. The system will suggest names for the ad group according to relevant keywords — see screenshot below— |
- You can filter the settings by location and language
- If you want, you can expand a group by clicking the + button, thus creating a sub-group based on one of the topics of the initial group.
2. The system analyzes web pages according to those keywords and topics
- Click the (…) in the group you want from figure 1 to see a list of predicted placements (where the platform will probably display your ads). Take your opportunity and remove any unwanted websites.
3. The platform displays the ads on relevant webpages.
Which Platforms of Contextual Targeting Should You Choose?
Contextual advertising is available from well-known advertising platforms and ad networks. Here are a few examples:
CodeFuel
This complete monetization platform uses contextual targeting to deliver highly relevant ads to high-intent users.
Key features
- Uses an intent-based search to monetize digital properties such as apps, extensions, and websites.
- Provides search mediation via optimized landing pages for media campaigns.
- Supports multiple media buys such as Facebook, Google, Taboola, and Outbrain).
- Presents shopping ads with high relevance to drive high-intent users into conversion.
- Leverages search ads with customized search results pages.
Pros
- Flexibility
- Centralized dashboard
- All-in-one solution
- Multiple integrations.
Cons
- Requires a mid-sized audience to find high-intent users.
Google Ads
This popular platform offers an extensive reach, serving ads based on searches and keywords. Google Ads allows publishers to monetize websites by presenting ads related to keyword searches.
Key features
- Analyzes your website and places ads based on the layout, content, and if you already have other Google ads.
- Automatically adapts the size of the ad to the user’s screen.
Pros
- Simple to use: you just need a Google Account and website
- Easy to use: you add the same line of code to each page you want to show ads.
- Responsive: adapts the ads automatically to mobile.
Cons
- Too wide a reach
- Restricts working with other ad networks. Use CodeFuel to access the premium Google ad network.
Yahoo! Bing Network
Bing provides contextual ads intending to help publishers to earn advertising revenue.
Key features
- Keyword-targeted advertisement
- High intent targeting
- Automatically generated ad units
- Mobile ads
Pros
- Ads are targeted to individual pages
- Customizable ads
- Additional control allows you to influence audience targeting, block ad topics, and filter advertisers.
Cons
- Requires a lot of traffic from top-tier countries
- Only offers payment in USD.
Contextual Targeting Examples
Contextual targeting is a very clever way of targeting viewers because it is tied to their interests. Let’s review some examples, so you have a clearer idea of how this works:
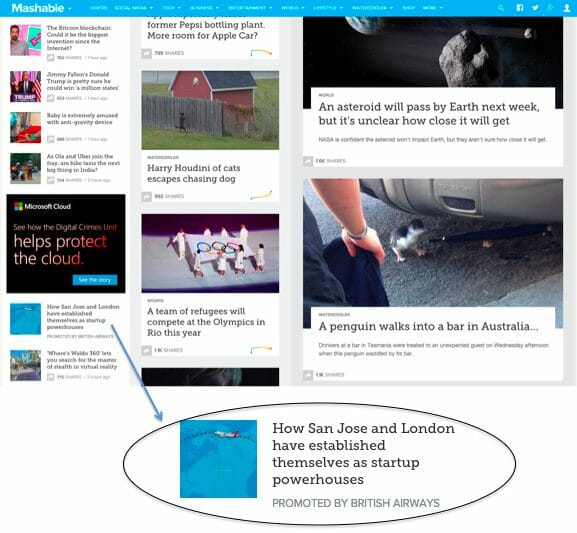
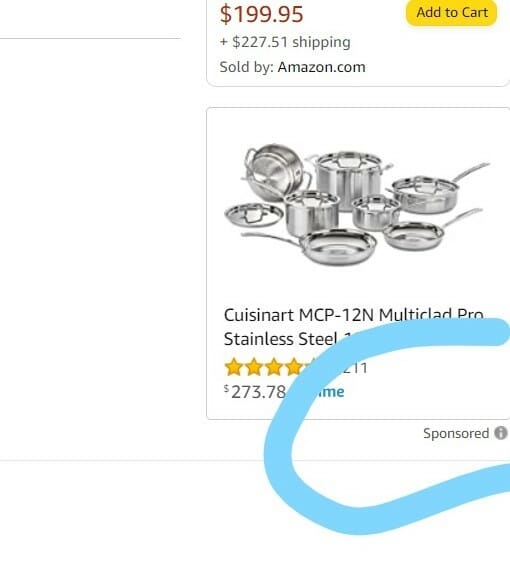
1. Ads about Dutch Ovens inside an article about Dutch Ovens
Epicurious is a well-known site for amateur cooks and features product reviews and comparisons regularly. This article was geared to inform the consumer how to choose a Dutch Oven. The piece features ads at the bottom with several options from well-known brands. The reader can buy with a quick link to the ad.
Source: Epicurious
2. Swimsuit ads besides workout and fitness content
Source: Fitness Blender
What isn’t clever about adding swimsuit ads on a fitness website?. While the consumers choose which workout to do, they can choose a swimsuit to go with their new fit body.
- Makeup ads when looking for makeup tutorials
When you search for a topic on YouTube, the platform presents you with a dynamic lineup, which offers ads to customers watching videos. It helps brands scale up by serving ads that enhance what they are viewing.
Difference Between Contextual and Behavioral Targeting
Until now, many marketers were comfortable relying on techniques like behavioral targeting. But with the phasing out of third-party cookies by 2022, marketers are looking for new ways of reaching their target audience.
Both contextual and behavioral targeting have the same goal: ensuring that the right ad is placed in front of the user who is most likely to purchase. The issue with behavioral targeting is that technique is based on past consumer behavior to predict future actions. On the other side, contextual targeting targets campaigns by placing ads on the website the buyer may end.
Contextual Targeting Pros and Cons
Now that we know more about contextual targeting, let’s explore the pros and cons. While it is more effective than other targeting methods, it has its challenges. Here is a summary of its benefits and challenges.
The pros of contextual targeting
- Keeps you compliant with regulations. Because it relies very little on personal data, contextual targeting helps align with regulations like GDPR with ease. Moreover, if you don’t collect personal data but only information about the website, then the targeting is outside the terms of the GDPR, and regulation doesn’t apply.
- Complement content. When done right, contextual ads enhance the user experience by adding timely information to the content. Some studies show contextual targeting may increase purchase intent by 63%.
- Are based in the interest of the user. For example, contextual ads in review sites increase the chance of getting clicked.
The cons of contextual targeting
- It requires attention. When setting up your ad campaign, you need to be careful, so the context is not too broad.
- There can be problems with frequency capping. Limiting how frequently a visitor to a website is shown a particular ad.
Why Is Contextual Targeting Now Popular Again?
You can use several methods to target your audience. Methods like personalized advertising or retargeting rely strongly on user data. Because of new regulations like GDPR, it is going to be difficult for advertisers. Both advertisers and publishers need to get consent from users to collect their data for audience targeting, which can be tricky.
Also, with third-party cookies disappearing in 2022, there is a bigger understanding of how contextual ad targeting can help without creating issues with data protection.
How does Contextual Targeting work in Social Media
Social media channels are full of ads, and it seems that the more businesses compete for attention, the more users filter out ads. That’s why context is so essential to create a better brand effect.
Social media contextual advertising is a model where users are targeted according to their browsing behavior. Ad networks extract content from social media websites and use artificial intelligence to analyze the audience and display relevant advertisements.
Social contextual marketing is growing thanks to the popularity of mobile social networks. The monetization of mobile social networks like Instagram is becoming a trend followed by other networks. Chat applications like Whatsapp and Facebook Messenger are not yet monetized. We Chat is the only application monetized so far.
Why is contextual targeting effective for social media? Because in social media, users naturally self-segment to participate on the platforms. That makes contextual advertising even more effective in reaching customers. The ever-increasing numbers of social media users are reason enough to start applying contextual targeting in your social media channels.
Best Practices for Digital Marketers
The goal of contextual targeting is to deliver highly personalized ads to users. The personalization factor of this marketing strategy is what makes contextual targeting so effective.
So, if you are looking to start with contextual targeting, look no further. Here are four best practices you can start implementing now.
1. The more you segment, the better
Create separate ad groups for each ad placed. That way, you can personalize the ads, targeting more people. Analyze your audience data so you can understand your target audience, segmenting them into smaller defined groups.
2. Use an array of ad types.
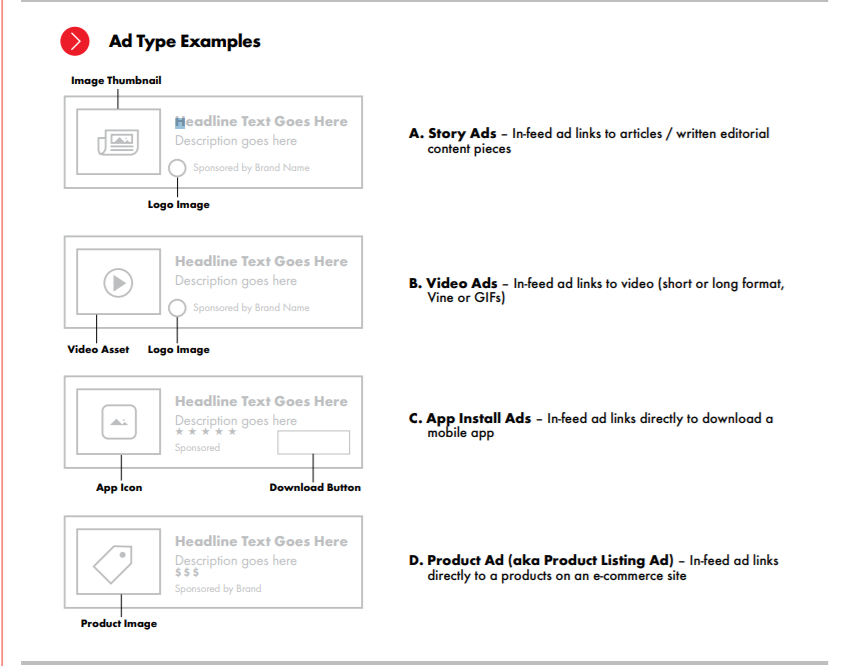
When you use various ad types for your contextual targeting campaign, you have more chances to deliver the right message to the user. Use a mix of video, native and behavioral ads for optimal results.
- Video ads: one of the best ways to engage your audience. When combined with contextual targeting, video ads are a powerful tool. If a YouTube user clicks on a video about applying makeup, they may receive an ad for makeup brands on that page or video.
- Native ads: these are the most popular type of ads present on contextual targeting. Native ads are designed, so they look like part of the page. They seem more relatable and increase the engagement of the user with your campaign.
- Behavioral ads: behavioral ads are tailored to a specific user based on their interests and online behaviors. Combining behavioral ads with contextual targeting helps you reach the right user with the right message at the right time.
3. Include a call to action
Make sure the user that sees the ad knows what action they should take. For instance,” shop now,” “click to learn more,” and so on. When the user can identify what is the next step when viewing the ad, they are more likely to take that action. Conversions are more likely when the ad copy relates closely to what they are looking to purchase.
4. Build an effective landing page
Relevance is the name of the game when it comes to contextual targeting. If you want to keep your campaign relevant, each ad should have its landing page. A unique landing page helps your users engage with your brand and encourage them to take action.
How Effective is Contextual Targeting?
According to a study, a lot. The research, conducted by neuro analytics company SPARK Neuro, aims to demonstrate how modern contextual advertising, with its components of machine learning and natural language processing (NLP), is a highly effective method for ad targeting.
The study showed users ads with different contextual relevance and measured their neuro activity, and looked on the page when reading the content. They found the contextually relevant ads generated 43% more engagement and two times more ad recall.
Another study that appeared in the International Journal of Advertising says that
“The results demonstrate that the internet contextual advertising enhances brand recognition and induces favorable attitudes towards the ad. (Are contextual advertisements effective?, IJA)
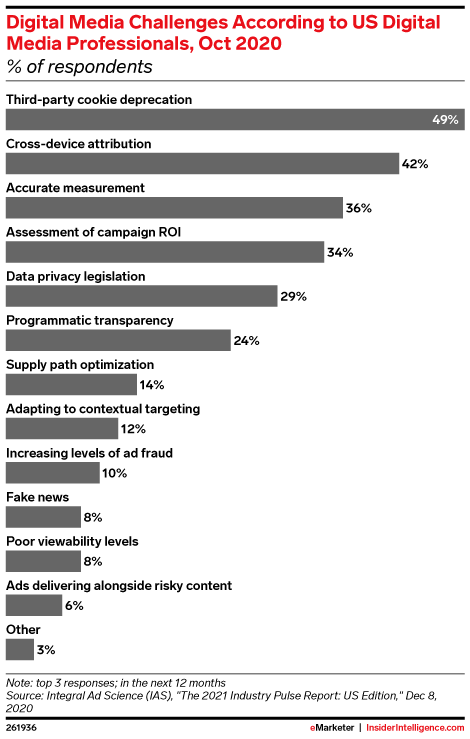
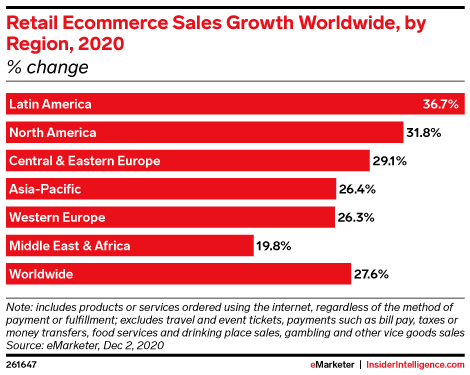
Contextual Targeting Statistics
- The phasing out of third-party cookies is a crucial challenge for US digital media professionals.
Source: emarketer
|
Why Contextual Targeting is the best solution for a Cookie-less Ad Market
Using contextual targeting with digital advertising (especially with display advertising) has several advantages;
1. It is highly relevant
Contextual targeting means that the person viewing your ads will be more interested in them because of the context of the page they are visiting. However, when ad creatives are not relevant, users can get tired. Advertisers then need to enhance the user experience with more relevant ads.
2. Prevents ad fatigue
An ad close to the right content can enhance the content and prevent getting tired of ads. The user doesn’t see them as sales but as helpful.
3. Privacy regulations friendly
Contextual targeting doesn’t interfere with user behavior; it is only about the page where the ad is placed. They don’t collect data on the viewer. Contextual targeting only uses the information on the content of the webpage.
Future Trends of Contextual Advertising
Contextual advertising may be around for a long time but is by no means static. Here are the top trends about contextual advertising that can help you stay informed:
1. Advances in relevance software
Developers wanting to improve the relevance of targeted ads just need to insert a JavaScript code into the webpage.
2. In-text video contextual advertising
New technologies allow placing in-video text advertisements on YouTube. Video-on-video ads are possible as well, with platforms working similarly to AdSense. They scan the video for content and propose advertising based on the content.
3. In-game contextual ads.
Developers tried with various degrees of success to insert contextual advertising in video games. When they would appear in the middle of a game it was very annoying for gamers. Inserting the ads before or after the games is more effective and less disruptive. Still, app developers need to monetize their applications. Therefore, developers are trying different ways to integrate contextual advertising without interfering with the user experience. For example, the game AdRacer, created by the University of Luxemburg presents ads on roadside virtual “billboards” as the player is driving.
FAQ’s About Contextual Targeting
How will contextual targeting look when cookies are phased out?
It has been argued that contextual targeting is the next step in digital advertising, answering the end of third-party cookies. Marketers will focus again on context marketing, which puts contextual targeting as an ideal approach. Leveraging context to deliver highly targeted advertisements can impulse contextual targeting to new popularity.
How can publishers maintain control of contextual advertising?
In a way, contextual advertising provides a lot of control for publishers. Publishers can tap on their high-quality content to monetize it accordingly. By leveraging an ad network or monetization platform that focuses on contextual advertising, publishers can regain value. By using contextual targeting, publishers enhance the user experience, better align ads to the page and increase engagement.
How do you build a contextually targeted campaign in Google Ads?
Google Ads uses contextual targeting to match keyword-targeted ads to sites in the Google Display Network. If you want to build a contextually targeted campaign in Google Ads here are a few pointers:
1. Define a specific theme for your ad group: each ad group should have its theme. Start with the theme that describes the product or service, and include branded keywords.
2. Be sure to include enough and relevant keywords: you can add between 5 and 50 keywords but be careful not to repeat keywords in the same ad group. Keep keywords relevant to the ad group theme.
3. Set the bids: the Display Network bid should be at the same level as your search bid.
4. Be efficient with negative keywords: this will prevent your ad from appearing on irrelevant sites, saving you money.
How CodeFuel uses Contextual Targeting to Increase Conversions
When contextual targeting is done right, it enables brands to reach their audiences in the right environment at the right time. CodeFuel solution offers contextual targeting capabilities that go beyond keyword or URL-based targeting. By leveraging AI, CodeFuel delivers high yields for publishers with an intent-based journey. It is easy to deploy, use and analyze results.
CodeFuel is a complete monetization platform geared to maximize publisher’s yield by delivering the highest relevance based on intent and advanced analytics. Start monetizing your digital property today. Sign up now.
Related Content To Read:
-
What is Contextual Advertising and How It Works: Examples with Pros and Cons
-
Monetize with Contextual Ads
-
What is Native Advertising and How it Works: Explained
-
Native Advertising vs. Display Advertising: When and How to Use Each
-
How To Apply For Google Adsense: Step by Step Guide
-
How to Make Money with Google Adsense